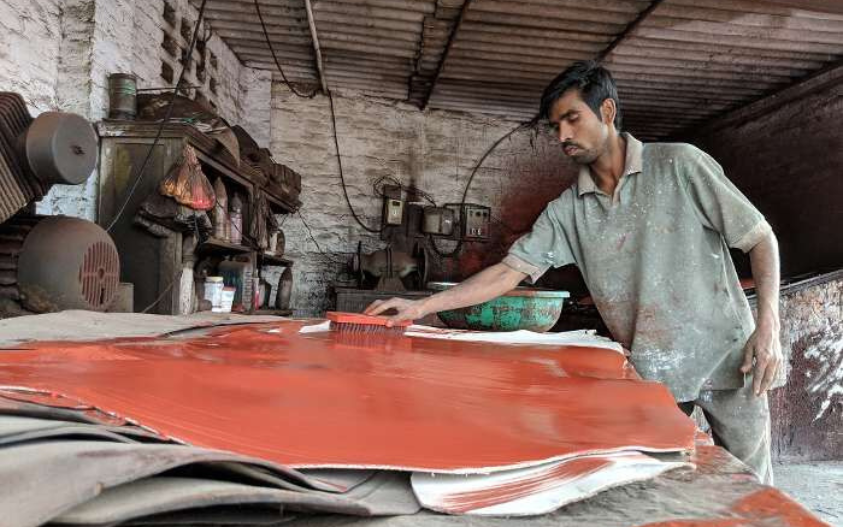
The Kanpur leather industry, despite its rich history and economic significance, faces several challenges that hinder its growth and sustainability. These issues span environmental concerns, regulatory compliance, financial constraints, labor challenges, and competition. Here’s an in-depth look at some of the main problems confronting the industry:
1. Environmental Pollution and Regulatory Compliance
- Water Pollution: One of the major environmental issues is water pollution, especially due to the discharge of untreated or partially treated effluents, including toxic chemicals like chromium, into the Ganges River. This has raised concerns among environmentalists, government agencies, and local communities.
- Air and Soil Pollution: Tanning releases hazardous gases and chemicals, which also impact air and soil quality around Kanpur. Chromium waste can seep into groundwater, creating health risks for residents.
- Regulatory Challenges: Compliance with environmental regulations, such as the Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) mandate, requires substantial investment in wastewater treatment and other eco-friendly technologies. Smaller tanneries find it financially difficult to meet these standards, and frequent regulatory inspections add pressure.
2. High Costs of Modernization and Technology
- Outdated Technology: Many tanneries and leather units in Kanpur still operate with outdated technology, which impacts productivity and product quality. The lack of modernization limits their ability to meet international quality standards.
- Financial Burden: Modernizing equipment and installing environmentally friendly machinery is costly, and smaller units often struggle to afford these upgrades. Even with government subsidies, the capital required for technology improvement can be a barrier for many businesses.
3. Skilled Labor Shortage and Workforce Challenges
- Limited Skill Development: The leather industry relies heavily on skilled labor for processes like tanning, stitching, and finishing. However, a shortage of skilled workers and insufficient training facilities result in a talent gap.
- Poor Working Conditions: The industry has been criticized for poor working conditions, especially in tanneries where workers are often exposed to chemicals without adequate protective equipment. These conditions make it difficult to retain labor and attract young workers to the sector.
- Low Wages and Job Insecurity: Workers in Kanpur’s leather industry are often underpaid, with limited job security and minimal benefits. This has led to high turnover and a lack of long-term commitment among employees.
4. Financial Constraints and Limited Access to Credit
- Many small- and medium-sized leather enterprises (SMEs) struggle to access financing for upgrades, expansion, and working capital. Banks are often reluctant to lend due to perceived risks associated with the industry’s environmental concerns and its cyclical demand.
- Without sufficient credit, businesses face difficulties in investing in technology, infrastructure, and eco-friendly measures. This hinders their ability to expand and become more competitive.
5. Intense Global and Domestic Competition
- Global Competition: Kanpur’s leather industry faces stiff competition from countries like China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, where production costs are lower and environmental regulations are often less stringent. This makes it challenging for Kanpur’s leather products to compete on price in international markets.
- Rise of Synthetic Alternatives: The increasing demand for synthetic and vegan leather alternatives, which are perceived as more sustainable, also presents a significant challenge. Many consumers, particularly in Western markets, are shifting towards cruelty-free and eco-friendly alternatives.
6. Inconsistent Power Supply and Infrastructure Issues
- Frequent power outages and unreliable infrastructure in Kanpur make production inefficient and increase operational costs. Many businesses have to rely on backup generators, which further raises expenses.
- Poor infrastructure in terms of road connectivity and transportation also hinders the supply chain, delaying shipments of raw materials and finished products.
7. Environmental and Compliance Costs
- Costs of Waste Management: Effluent treatment plants and solid waste management systems require significant investment, which small tanneries struggle to afford.
- Regulatory Pressures: Frequent inspections and strict environmental mandates, such as the requirement for Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs), increase compliance costs. Failing to comply with regulations can lead to fines, shutdowns, and reputation damage.
8. Limited Innovation and Product Diversification
- Low Innovation Levels: The industry lacks innovation in product design, manufacturing techniques, and environmental solutions, leading to reduced competitiveness in the global market.
- Lack of Diversification: Many units focus primarily on traditional products like shoes and saddlery, with limited product diversification. This restricts the industry’s ability to tap into high-value markets such as luxury leather goods, which require advanced skills and technology.
9. Lack of Branding and Global Market Presence
- The Kanpur leather industry suffers from a lack of branding and global presence, which makes it difficult to establish a reputation in high-end markets. Without strong branding, Kanpur’s leather products are often perceived as low-value items, even when quality matches international standards.
- Limited participation in international trade fairs, exhibitions, and marketing initiatives also affects market reach and consumer awareness of Kanpur’s leather products.
10. Complex Supply Chain and Raw Material Issues
- Volatile Raw Material Prices: Leather production depends on animal hides, and fluctuations in raw material prices can affect profitability. Price volatility is often influenced by supply-demand imbalances, currency exchange rates, and transportation issues.
- Quality of Raw Materials: Access to high-quality raw hides is crucial, but quality inconsistency and inadequate storage facilities can lead to product quality issues, impacting the final output and international competitiveness.
In Summary:
The Kanpur leather industry’s future depends on addressing these challenges through sustainable practices, modernization, skill development, and effective branding. Government support, combined with industry efforts to innovate, diversify, and improve compliance, will be essential for the industry’s long-term growth and competitiveness.