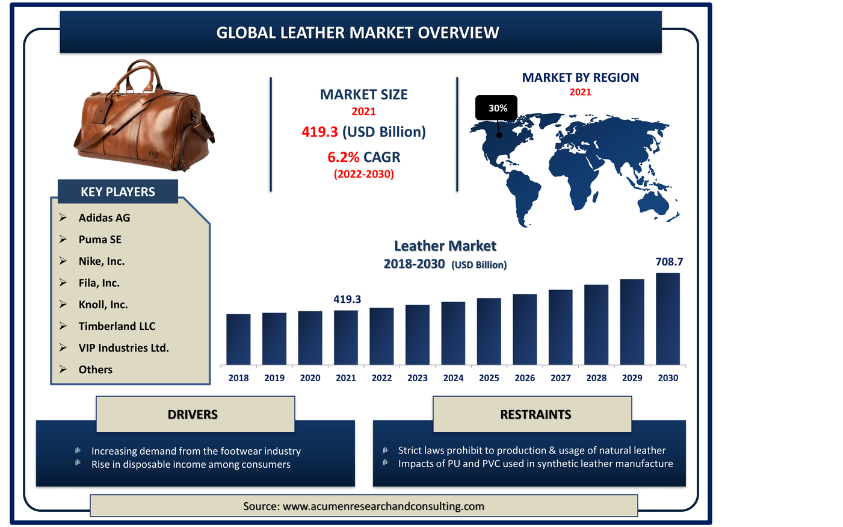
The Import-Export Index for the leather industry refers to the indicators, statistics, and trends that track leather imports and exports globally and domestically. India, as one of the world’s leading producers and exporters of leather and leather products, has significant data on its export performance in this sector, including insights into key markets, export trends, and factors affecting import and export growth. Here’s an overview of the current import-export situation in the leather industry, with a focus on India:
1. India’s Leather Export Trends
- Global Market Position: India ranks among the top exporters of leather and leather products globally, alongside countries like China, Italy, Vietnam, and Brazil. It accounts for approximately 10% of the global leather trade.
- Key Export Products: India primarily exports finished leather, footwear, leather goods (bags, wallets), leather garments, and accessories. Footwear is the largest segment, accounting for over 40% of India’s leather exports.
- Top Export Markets: The European Union is the largest market for Indian leather products, with countries like Germany, Italy, and the UK being major importers. The United States, United Arab Emirates, China, and Australia are also significant markets.
2. Leather Import Trends in India
- Raw Materials: India imports certain types of raw hides and skins that are not readily available domestically or are of higher quality. These are primarily imported from countries such as Italy, Germany, and the USA.
- Machinery and Chemicals: India imports advanced leather processing machinery and specialty chemicals, primarily from Europe and East Asia, to meet the requirements of modern leather manufacturing.
3. Export Growth and Market Share
- Annual Growth: The leather and leather product export sector in India has grown at an average annual rate of around 3-5% over recent years, with footwear exports leading this growth. However, the growth rate has been impacted by global challenges, including economic slowdowns, trade restrictions, and the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Rising Demand for Sustainable Leather: There is an increasing demand for eco-friendly and sustainably produced leather goods, which has led to growth in markets for “green” leather products. This demand is driving Indian leather exporters to adopt sustainable practices.
4. Import-Export Balance and Trade Surplus
- Trade Surplus: India’s leather industry operates at a trade surplus, with exports far exceeding imports. Exports are primarily high-value finished goods, while imports are generally raw materials, machinery, and chemicals necessary for production.
- Import Substitution and Self-Sufficiency: The government’s focus on boosting domestic production and reducing reliance on imported raw materials through the “Make in India” initiative has led to a reduction in imports of certain materials and equipment.
5. Key Challenges Affecting Import-Export Performance
- Environmental Compliance and Sustainability: Many importers, especially in Europe, have stringent environmental and quality standards, which can be challenging for Indian exporters due to high compliance costs.
- Competition: India’s leather exports face intense competition from countries like China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, where production costs are lower.
- Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Trade tariffs imposed by importing countries and trade barriers, especially in regions like Europe and North America, impact export prices and profitability.
6. Impact of Government Policies on Import-Export Index
- Incentives and Schemes: The Indian government offers incentives such as the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) and subsidies under the Indian Footwear, Leather, and Accessories Development Programme (IFLADP). These policies help boost exports by reducing costs for exporters.
- Export Quality and Standards: Through agencies like the Leather Sector Export Promotion Council (CLE), the government supports exporters in meeting international standards, which improves market access.
7. Recent Developments and Trends
- Post-COVID Recovery: Leather exports have seen a rebound as global demand for leather goods increases. However, ongoing supply chain issues and inflationary pressures continue to affect the cost of materials.
- Focus on Premium Markets: India’s leather industry is gradually moving towards producing more high-end and premium products to meet demand in developed markets, improving the export value per unit.
- Rising Demand for Non-Animal Leather: Synthetic and “vegan” leather products are gaining popularity, especially in Western markets. This trend poses a threat to traditional leather exports but also presents an opportunity to diversify products.
8. Current Export Statistics
- Annual Export Value: India’s leather industry exports are valued at approximately $5-6 billion annually, with footwear, leather goods, and leather apparel making up the majority of this figure.
- Share of Global Exports: India holds around 2-3% of the global leather and leather products market in terms of value, making it one of the key global exporters.
Summary
India’s leather import-export index shows a strong performance in exports, with footwear and finished leather goods leading the sector. The country maintains a trade surplus, leveraging government incentives and demand from international markets. However, the industry faces challenges from global competition, stringent environmental standards, and shifting consumer preferences toward sustainable and synthetic leather alternatives. The future of India’s leather import-export dynamics will depend on innovation, sustainable practices, and successful navigation of global trade complexities.